The lipid-lowering effect of almonds
10/25/2018 / By Michelle Simmons

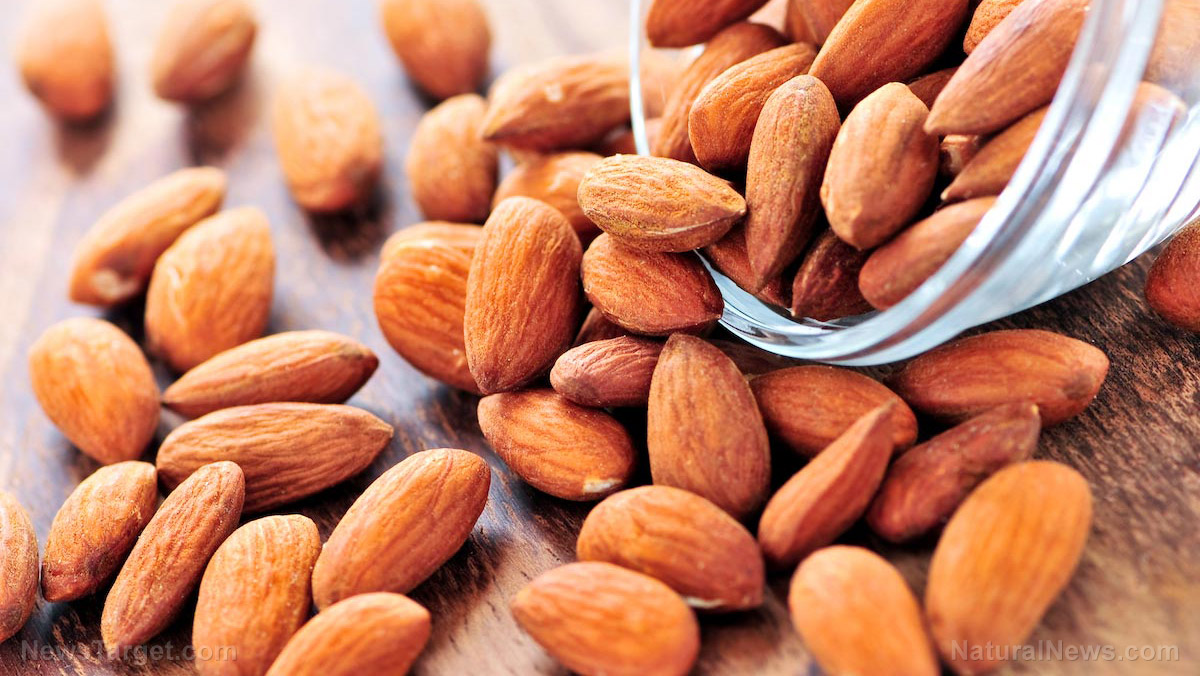
Regular consumption of almonds can help improve lipid profiles and body composition of healthy young adults, according to a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food. In the study, researchers from Sookmyung Women’s University and ICAN Nutrition Education and Research in Seoul, South Korea examined the effects of daily almond consumption on lipid profiles and body composition.
- Earlier research has shown that almonds offer many health benefits, especially in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
- Some of the participants in the study consumed 56 grams of almonds per day, while others were given carbohydrate-rich control food items that had a similar number of calories as 56 g of almonds.
- The intervention period lasted for 20 weeks and participants were instructed to maintain their habitual dietary intake and usual physical activity and refrain from eating additional nuts or nut products throughout the study period.
- The researchers measured the changes in lipid profiles and body composition of the participants before the intervention, at the eighth week, 16th week, and 20th week of the intervention.
- The results showed that participants who consumed almonds every day for 20 weeks exhibited significant reductions in blood lipid profiles, such as levels of triglycerides, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and non-high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL) cholesterol.
- They also experienced decreases in body fat mass and waist-hip ratio.
Overall, the findings of the study indicate that daily consumption of almonds can help improve lipid profiles and body composition.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
To read more stories on foods that keep you healthy, visit Superfoods.news today.
Journal Reference:
Liu Y, Hang HJ, Kim HS, Park H. TIME AND INTERVENTION EFFECTS OF DAILY ALMOND INTAKE ON THE CHANGES OF LIPID PROFILE AND BODY COMPOSITION AMONG FREE-LIVING HEALTHY ADULTS. Journal of Medicinal Food. 1 April 2018; 21(4). DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2017.3976
Tagged Under: almonds, bad cholesterol, belly fat, Body composition, cholesterol, cholesterol level, good cholesterol, Lipid profile, nuts, triglycerides